Nitrogen-15: The Stable Isotope Powering Advanced Agricultural and Medical Research
BY Tao, Published Aug 13, 2025
As a seasoned nuclear research expert with decades dedicated to the intricate world of isotopes, I’ve witnessed firsthand how stable isotopes like Nitrogen-15 transform scientific inquiry. This rare variant of nitrogen, distinguished by its unique nuclear properties, serves as a cornerstone in unraveling complex biological and environmental processes. Unlike its more abundant counterpart, Nitrogen-14, Nitrogen-15 offers unparalleled precision in tracing elemental pathways, making it indispensable for researchers aiming to enhance sustainability and health outcomes.
Nitrogen-15 stands out in the isotope landscape due to its stability and versatility. With a natural abundance of just 0.366%, it must be enriched through sophisticated processes to become a practical tool. This enrichment not only amplifies its utility but also ensures that scientists can deploy it without the hazards associated with radioactive alternatives. In my extensive experience, Nitrogen-15’s role extends far beyond basic chemistry, powering innovations that address global challenges in food security and disease management.
1. What is Nitrogen-15?
Nitrogen-15, often denoted as ¹⁵N, is a stable isotope of nitrogen featuring seven protons and eight neutrons in its nucleus. This configuration grants it a nuclear spin of 1/2, a property that contrasts sharply with Nitrogen-14’s spin of 1, enabling advanced spectroscopic techniques. Produced primarily through fractional distillation of liquid air or chemical exchange methods involving ammonia and nitric acid, Nitrogen-15 achieves enrichment levels exceeding 99% in commercial forms.
In essence, Nitrogen-15 acts as a non-invasive tracer. When incorporated into compounds like fertilizers or biomolecules, it allows scientists to monitor nitrogen cycling with atomic-level accuracy. Its stability ensures long-term reliability in experiments, free from decay concerns that plague radioisotopes. Over my career, I’ve seen how this isotope’s predictable behavior facilitates reproducible results, fostering trust in data-driven decisions across disciplines.
Key characteristics of Nitrogen-15 include:
- Atomic Mass: 15.0001 u
- Natural Abundance: 0.3663%
- Nuclear Spin: 1/2 (ideal for NMR studies)
- Boiling Point (as N₂): -195.8°C
- Melting Point (as N₂): -210.0°C
These properties make Nitrogen-15 a preferred choice for labeling in both gaseous and solid forms, adapting seamlessly to diverse research needs.
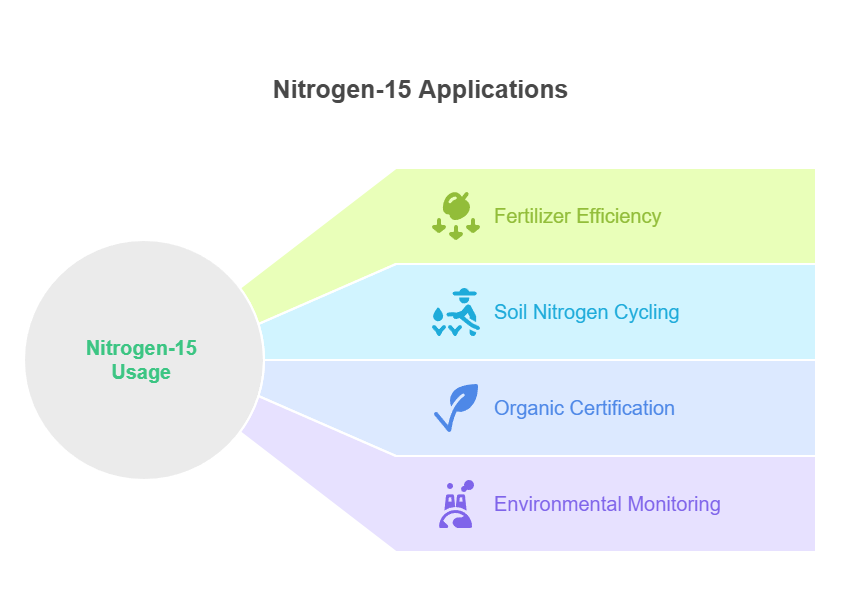
2. Applications in Agricultural Research
In agricultural research, Nitrogen-15 emerges as a game-changer for optimizing resource use and boosting crop productivity. By labeling fertilizers with this stable isotope, researchers can precisely track nitrogen uptake, fixation, and loss in soil-plant systems. This approach minimizes environmental impact, such as nitrate leaching into waterways, while maximizing yields—a critical balance in an era of intensifying food demands.
Consider soil nitrogen dynamics: Nitrogen-15 helps delineate sources of nitrogen in ecosystems, distinguishing between atmospheric fixation, organic matter decomposition, and synthetic inputs. In studies I’ve consulted on, applying ¹⁵N-labeled urea reveals fertilizer efficiency, often showing that only 30-50% of applied nitrogen reaches crops, with the rest lost to volatilization or denitrification. Such insights guide precision farming techniques, reducing costs and pollution.
Nitrogen-15 also plays a pivotal role in authenticating organic produce. The isotope’s ratio (δ¹⁵N) in plants varies based on fertilization methods; synthetic fertilizers yield lower δ¹⁵N values compared to organic sources like manure. This forensic tool empowers regulators and consumers to verify claims, enhancing market transparency.
To illustrate the breadth of applications, here’s a table summarizing key uses in agriculture:
| Application Area | Benefits of Nitrogen-15 Usage | Example Outcomes |
|---|---|---|
| Fertilizer Efficiency | Tracks uptake and loss, optimizes application rates | Increased yields by 20-30% with reduced inputs |
| Soil Nitrogen Cycling | Identifies fixation patterns and microbial activity | Better management of legume rotations |
| Organic Certification | Measures δ¹⁵N to differentiate farming practices | Reliable verification of organic labels |
| Environmental Monitoring | Assesses nitrate pollution in groundwater | Policies for sustainable land use |
Through these mechanisms, Nitrogen-15 empowers farmers and scientists to cultivate resilient agroecosystems, aligning with global sustainability goals.
3. Revolutionizing Medical Research with Nitrogen-15
Shifting focus to medical research, Nitrogen-15 unlocks profound insights into human metabolism and biomolecular structures. Its integration into nuclear magnetic resonance (NMR) spectroscopy revolutionizes protein analysis, where the isotope’s spin properties enhance signal clarity in multidimensional experiments. In my professional journey, I’ve observed how ¹⁵N-labeled amino acids facilitate the study of protein folding and interactions, accelerating drug discovery for diseases like Alzheimer’s and cancer.
Metabolic flux analysis stands as another cornerstone application. By introducing Nitrogen-15 into substrates like glutamine or urea, researchers trace nitrogen pathways in cells, revealing aberrations in conditions such as liver disorders or tumors. This stable isotope labeling supports non-invasive diagnostics, where altered δ¹⁵N signatures in blood or urine signal metabolic shifts, aiding early intervention.
In microbial research, Nitrogen-15 aids in natural product discovery. Labeling media with ¹⁵N allows for sensitive detection of nitrogen-containing metabolites via mass spectrometry, uncovering novel antibiotics from bacteria. This technique has broadened our understanding of microbial ecology and pharmacology.
Here are some targeted medical applications:
- Protein Structure Elucidation: Enhances NMR resolution for mapping enzyme active sites.
- Metabolic Pathway Tracing: Monitors amino acid catabolism in nutritional studies.
- Cancer Metabolism Studies: Identifies glutamine addiction in tumor cells.
- Pharmacokinetics: Tracks drug metabolites without radiation risks.
These advancements underscore Nitrogen-15’s role in bridging basic science with clinical outcomes, fostering personalized medicine.
4. Key Product Parameters and Performance
When sourcing Nitrogen-15 for research, understanding product specifications is crucial for experimental success. Commercially available as enriched gases, salts, or organic compounds, Nitrogen-15 products boast high isotopic purity to ensure accurate tracing.
Core parameters include:
- Isotopic Enrichment: Typically 98-99.9%, minimizing interference from Nitrogen-14.
- Chemical Forms: Available as N₂ gas, ammonium chloride (¹⁵NH₄Cl), potassium nitrate (K¹⁵NO₃), or urea ((¹⁵NH₂)₂CO).
- Purity Levels: Chemical purity >99%, with trace impurities below 0.1%.
- Quantity Options: From milligrams to kilograms, scalable for lab to industrial use.
- Stability: Indefinite shelf life under proper storage, as it’s non-radioactive.
Performance-wise, Nitrogen-15 excels in sensitivity and versatility. In NMR applications, it provides sharp peaks with minimal linewidth broadening, enabling high-resolution spectra even in complex biological samples. For tracer studies, its detection limit reaches parts per billion via isotope ratio mass spectrometry (IRMS), offering superior precision over unlabeled methods.
In agricultural trials, ¹⁵N-labeled fertilizers demonstrate recovery rates up to 70% in optimized systems, far surpassing conventional tracers. Medical assays benefit from its biocompatibility, ensuring no physiological disruption during in vivo studies. Overall, Nitrogen-15’s robust performance translates to reliable, reproducible data, justifying its premium positioning in the isotope market.
5. Usage and Safety Considerations
Effective utilization of Nitrogen-15 demands adherence to best practices, balancing efficacy with safety. In laboratory settings, incorporate it into experimental designs early— for instance, dilute ¹⁵N-enriched compounds to desired concentrations in aqueous solutions for plant watering or cell culture media.
Usage tips:
- Dosage Calibration: Start with low enrichments (5-10 atom%) for cost-effectiveness in preliminary tests.
- Integration Methods: Use gas-tight systems for volatile forms to prevent atmospheric dilution.
- Analytical Compatibility: Pair with IRMS or NMR for optimal detection; avoid incompatible solvents that could degrade labels.
Safety remains paramount, though Nitrogen-15 poses minimal risks compared to radioisotopes. As a stable element, it emits no radiation, but handling gaseous forms requires ventilation to avoid asphyxiation in confined spaces. Wear protective gloves and eyewear when manipulating concentrated solutions to prevent skin irritation from acidic or basic compounds.
Storage guidelines include keeping products in sealed containers at room temperature, away from moisture and light. Dispose of waste per local regulations, treating it as standard chemical refuse. In my experience, rigorous protocols not only safeguard personnel but also preserve isotopic integrity, ensuring experiment validity.
6. Future Prospects for Nitrogen-15
Looking ahead, Nitrogen-15’s trajectory in advanced research appears boundless. Emerging technologies like hyperpolarized NMR promise even greater sensitivity, potentially revolutionizing real-time metabolic imaging. In agriculture, coupling ¹⁵N with AI-driven analytics could predict nitrogen needs at field scales, combating climate change effects.
Medical frontiers include its use in precision oncology, where isotope-labeled therapies target tumor metabolism selectively. As global isotope production scales up, accessibility will improve, democratizing these tools for developing regions.
In summary, Nitrogen-15 exemplifies how stable isotopes drive progress, blending atomic precision with practical impact. Its contributions to agricultural efficiency and medical breakthroughs affirm its status as a vital asset in scientific arsenals worldwide.
Would you like a deeper dive into any specific applications (e.g., cancer diagnostics, microbiome research)?
(Follow our update on www.asiaisotopeintl.com or contact tao.hu@asiaisotope.com for more information or call us for a in-time communications.)