Market Demand and Supply Trends for Carbon-13 Labeled Gas (¹³CO₂) in 2025
BY Tao, Published Aug 12, 2025
1. Overview of the Global Market for ¹³CO₂
Carbon-13 labeled gas, specifically ¹³CO₂, has emerged as a vital component in the stable isotopes sector, driven by its unique role in tracing carbon pathways across diverse industries. As a non-radioactive isotopic variant of carbon dioxide, ¹³CO₂ offers precise, safe labeling capabilities that are indispensable in modern scientific and industrial applications. In my extensive career studying gas isotopes and carbon-oxygen compounds, I’ve observed a steady escalation in demand for this specialized gas, fueled by advancements in medical diagnostics, environmental monitoring, and agricultural research. The global market for ¹³CO₂ is experiencing robust growth, with projections indicating a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) exceeding 20% through the early 2030s, reflecting its integration into high-value sectors.
The market’s expansion is underpinned by increasing awareness of sustainable practices and the need for accurate isotopic tracing. In 2024, the market value for carbon-13 gas, including ¹³CO₂, was estimated around 450 million USD, with expectations to surpass 1.9 billion USD by 2031. This surge is attributed to heightened investments in research and development, particularly in regions like North America and Europe, where regulatory frameworks emphasize precision in carbon-related studies. Asia-Pacific is also rising as a key player, with emerging economies ramping up production to meet local demands in biotechnology and ecology. Supply chains, however, face challenges from raw material sourcing and enrichment processes, which require sophisticated technologies to achieve high isotopic purity.
2. Key Drivers of Market Demand
Demand for ¹³CO₂ is propelled by its versatility in applications that require non-invasive, high-resolution tracing. In the medical sector, it’s extensively used in breath tests for detecting conditions like Helicobacter pylori infections and metabolic disorders, where patients ingest ¹³C-labeled compounds, and exhaled ¹³CO₂ is analyzed for diagnostic insights. This application alone accounts for a significant portion of market growth, as global healthcare systems prioritize early detection and personalized medicine.

Carbon-13 dioxide (¹³CO₂) in different volume Cylinders
Agriculture and ecology represent another major demand driver, with ¹³CO₂ employed to study soil carbon sequestration, plant photosynthesis efficiency, and ecosystem carbon fluxes. Farmers and researchers utilize it to optimize crop yields under climate stress, tracing how carbon moves from atmosphere to roots and soil microbes. Environmental research leverages ¹³CO₂ for modeling greenhouse gas dynamics, distinguishing biogenic from anthropogenic sources in atmospheric studies. The push toward sustainable farming and carbon-neutral policies has amplified this demand, especially with international agreements targeting net-zero emissions.
Additional factors influencing demand include:
- Pharmaceutical Research: ¹³CO₂ labels compounds for nuclear magnetic resonance (NMR) spectroscopy, accelerating drug development by providing detailed molecular structures.
- Industrial Processes: In petrochemicals and biofuels, it traces reaction mechanisms, enhancing efficiency in carbon conversion technologies.
- Regulatory Compliance: Stricter environmental regulations mandate precise carbon tracking, boosting adoption in monitoring programs.
- Technological Advancements: Integration with AI-driven analytics and laser-based detection systems expands its utility, creating new market niches.
These drivers collectively contribute to a demand trajectory that outpaces general industrial gases, with annual growth rates in specific segments reaching 25% or more.
3. Supply Trends and Major Players
On the supply side, the ¹³CO₂ market is characterized by a concentrated landscape dominated by specialized producers who excel in isotopic enrichment. Production involves complex methods like cryogenic distillation or laser separation to isolate ¹³C from natural CO₂ sources, often requiring significant capital investment in facilities equipped for handling rare gases and fluorocarbon intermediates. Global supply has seen improvements in efficiency, with advancements in chemical conversion techniques reducing costs and increasing output volumes.
Leading suppliers include multinational corporations with expertise in industrial gases, such as Linde, Air Liquide, and Air Products, which have expanded their portfolios to include stable isotopes through dedicated divisions. These companies leverage vast distribution networks to ensure timely delivery, often customizing ¹³CO₂ enrichments for client needs. Specialized firms like Cambridge Isotope Laboratories and Merck’s isotope arm focus on high-purity variants, catering to research-intensive markets. In Asia, players like Taiyo Nippon Sanso are gaining traction, investing in regional production hubs to mitigate supply chain disruptions.
Current trends in supply include:
- Capacity Expansion: Suppliers are scaling up facilities, with new plants in Europe and North America projected to add 15-20% to global capacity by 2027.
- Sustainability Focus: Emphasis on green production methods, such as using renewable energy for enrichment processes, aligns with buyer preferences for low-carbon footprints.
- Price Dynamics: Average prices for high-purity ¹³CO₂ influenced by enrichment levels and volume, with stabilization expected as supply catches up.
- Geopolitical Influences: Trade tensions and raw material shortages occasionally strain supplies, prompting diversification in sourcing.
Overall, supply is keeping pace with demand, though bottlenecks in ultra-high-purity grades persist, encouraging innovation in mixed gas formulations.
4. Regional Market Insights
Geographically, North America leads in both demand and supply, accounting for over 40% of the global market share due to robust R&D infrastructure and government funding for isotopic research. The United States, in particular, drives consumption through agencies focused on environmental and health sciences. Europe follows closely, with strong demand from pharmaceutical hubs in Germany and the UK, where ¹³CO₂ supports advanced NMR and breath analysis.
Asia-Pacific is the fastest-growing region, with a CAGR approaching 25%, spurred by agricultural modernization in China and India. Here, supply trends involve local partnerships to build enrichment capabilities, reducing reliance on imports. Latin America and the Middle East show emerging potential, primarily in ecology-driven applications for carbon sequestration in tropical ecosystems.
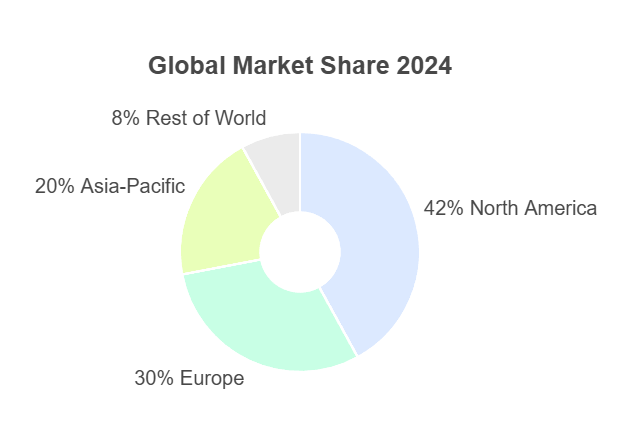
A comparative table of regional trends:
| Region | Market Share (2024) | Projected CAGR (2025-2031) | Key Demand Drivers | Supply Challenges |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| North America | 42% | 18% | Medical diagnostics, research | High production costs |
| Europe | 30% | 20% | Pharmaceuticals, environmental | Regulatory hurdles |
| Asia-Pacific | 20% | 25% | Agriculture, industrial processes | Infrastructure development |
| Rest of World | 8% | 15% | Ecology studies | Logistical issues |
This distribution highlights opportunities for suppliers to target high-growth areas while addressing regional specificities.
5. Product Specifications and Parameters
Understanding the specifications of ¹³CO₂ is essential for stakeholders navigating the market. This gas is typically supplied in compressed form within aluminum or steel cylinders, designed for safe transport and storage. Key parameters focus on isotopic and chemical purity to ensure reliability in applications.
Standard product details include:
| Parameter | Typical Value | Description |
|---|---|---|
| Isotopic Enrichment | 99% or higher atom % ¹³C | Critical for accurate tracing without dilution |
| Chemical Purity | ≥99.99% | Limits contaminants like O₂, N₂, or H₂O |
| Molecular Weight | Approximately 45 g/mol | Reflects the isotopic mass difference |
| Cylinder Pressure | 10-50 bar at 20°C | Ensures stable delivery for lab or field use |
| Volume Availability | 0.5-50 liters | From small research bottles to bulk supplies |
| Impurity Levels | <5 ppm for water, <2 ppm for oxygen | Prevents degradation during storage |
| Certification | Mass spectrometry verified | Includes δ¹³C values for traceability |
These specs are tailored to meet industry standards, with options for custom mixtures incorporating other carbon-oxygen gases or rare isotopes.
6. Performance Characteristics and Usage Considerations
¹³CO₂ exhibits exceptional performance as a stable tracer, maintaining isotopic integrity over extended periods, which is vital for long-term studies. Its non-reactivity under ambient conditions allows for seamless integration into biological and environmental systems, providing high-sensitivity detection in instruments like IRMS or NMR. Performance metrics often show detection limits at parts-per-billion levels, with minimal fractionation during handling.
In usage, prioritize safety protocols given its potential as an asphyxiant in confined spaces. Store in cool, dry environments (15-25°C) to preserve purity, and use dedicated regulators to avoid contamination. For medical applications, ensure sterile handling and precise dosing—typically 50-100 mg in breath tests—to achieve optimal exhalation signals.
Best practices encompass:
- Handling Guidelines: Wear protective gear and monitor ambient CO₂ levels during release.
- Compatibility Checks: Verify integration with analytical equipment to prevent isotopic mixing.
- Storage Tips: Avoid exposure to moisture or reactive metals, which could form unwanted compounds.
- Disposal Methods: Vent safely or recycle through certified facilities to minimize environmental impact.
Adhering to these enhances the gas’s performance, drawing from established norms in special gases management.
7. Challenges and Opportunities in the Market
Despite strong growth, the ¹³CO₂ market faces hurdles like high production costs and limited raw material availability, which can lead to price volatility. Supply chain disruptions, exacerbated by global events, underscore the need for diversified sourcing. However, opportunities abound in emerging applications, such as carbon capture utilization and storage (CCUS), where ¹³CO₂ traces efficiency in sequestration projects.
Innovation in production, including hybrid enrichment techniques combining cryogenic and chemical methods, promises to lower barriers and expand access. Collaborations between suppliers and end-users are fostering customized solutions, further stimulating market dynamics.
8. Future Outlook and Strategic Recommendations
Looking ahead to 2025 and beyond, the ¹³CO₂ market is poised for exponential growth, potentially reaching values over 2 billion USD , as sustainability imperatives intensify. Demand will likely surge in green technologies, with supply adapting through technological upgrades and strategic alliances. For businesses, investing in high-purity capabilities and regional expansion will be key to capitalizing on this trend. As an expert in nuclear elements, I anticipate ¹³CO₂ will continue to underpin breakthroughs in carbon science, shaping a more precise and sustainable future.
Would you like a deeper dive into any specific applications (e.g., cancer diagnostics, microbiome research)?
(Follow our update on www.asiaisotopeintl.com or contact tao.hu@asiaisotope.com for more information or call us for a in-time communications.)